The Future of Textile Recycling
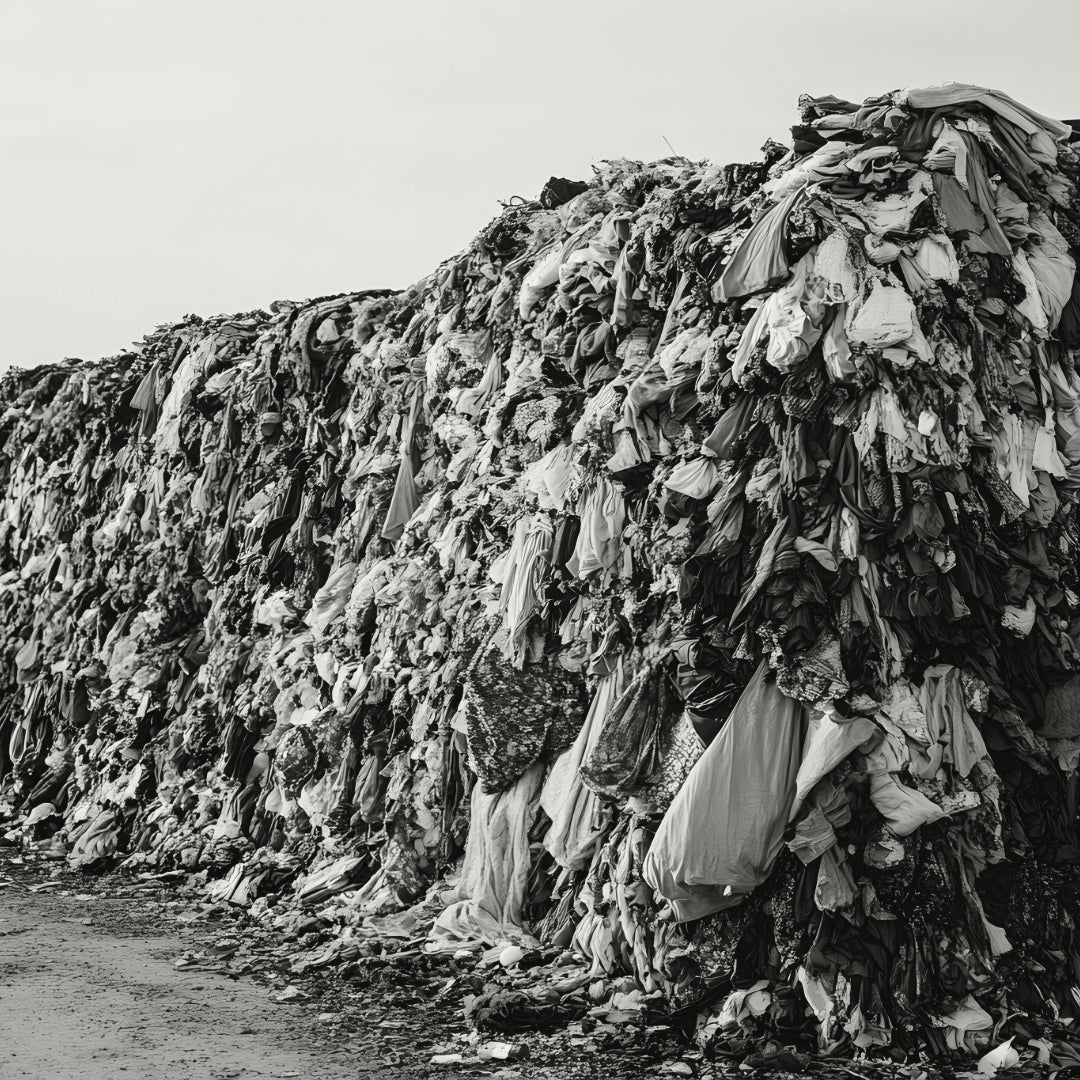

The Challenge
The textile industry is responsible for 10% of global CO₂ emissions, with over 140 million tons of textiles produced annually. Shockingly, 95% of these textiles are not recycled, they end up in landfills or are incinerated. With new EU legislation coming into force in 2025, prohibiting incineration and mandating producer responsibility and textile collection, millions of tons of discarded textiles will soon be collected.
The question remains: What do we do with it?

Our Solution
At CelluCircle, we've developed a proprietary chemical recycling process designed for large-scale operations. Our high feedstock tolerance allows us to process polycotton blends, synthetic fibers, and other challenging materials. The result, high-value outputs such as nanocellulose, nano-composites, original polyester fibers, and materials suitable for injection molding, 3D printing, and industrial applications. Our technology is water-based, uses mild chemicals, and operates with low energy consumption, ensuring minimal environmental impact.
The Vision
Our journey is only just beginning. With pilot facilities operational by 2025 and plans for EU and global scale-up shortly after, CelluCircle aims to lead the charge in sustainable textile recycling. Through strategic partnerships, innovation, and a commitment to a circular economy, we're transforming waste into valuable resources.
Join us as we redefine the future of textiles.
News
View all-

MP Group Holdings invests in CelluCircle to acc...
We are proud to announce that we have received a strategic investment from MP Group Holdings, a private investment firm focused on scaling purpose-driven ventures across healthcare, education, technology, consumer...
MP Group Holdings invests in CelluCircle to acc...
We are proud to announce that we have received a strategic investment from MP Group Holdings, a private investment firm focused on scaling purpose-driven ventures across healthcare, education, technology, consumer...
-

Closing 2025 with Innovation & Collaboration
Just before the year shift, we had the chance to close 2025 by hosting Vesa Hiltula, Arunas Paukste, and Tommy Johansson from Telge Återvinning at our R&D premises.We discussed textile sorting and organised a small demo...
Closing 2025 with Innovation & Collaboration
Just before the year shift, we had the chance to close 2025 by hosting Vesa Hiltula, Arunas Paukste, and Tommy Johansson from Telge Återvinning at our R&D premises.We discussed textile sorting and organised a small demo...
-

Meet Our New Process Engineers Powering CelluCi...
We’re excited to welcome Timo Maron and Konstantinos Apostolopoulos to CelluCircle as Process Engineers. Both will play key roles in designing, scaling, and optimizing our first pilot facility, an important...
Meet Our New Process Engineers Powering CelluCi...
We’re excited to welcome Timo Maron and Konstantinos Apostolopoulos to CelluCircle as Process Engineers. Both will play key roles in designing, scaling, and optimizing our first pilot facility, an important...



